The All-in-One Health Companion on Your Wrist:
The HUAWEI WATCH D2

Reading duration: Approximately 8 minutes

Daniel M. Plecity
Dr. Daniel M. Plecity is a senior consultant at a teaching hospital near Munich, Germany, and specialises in internal medicine, gastroenterology and oncology. With many years of experience in medical practice and training young doctors, he has in-depth knowledge in the fields of medical tumour therapy and nutritional medicine. As a keen triathlete and watch enthusiast, he combines his professional expertise with an active lifestyle.
In this article
Identifying the Possibility of High Blood Pressure - 24-Hour Blood Pressure Measurement with a Smartwatch
Blood Pressure Measurement Day and Night - The Practical Test
What to Do if You Have High Blood Pressure
Can the HUAWEI WATCH D2 help with weight loss?
What Else Can the HUAWEI WATCH D2 Do?
Conclusion: A Useful ‘Health Tool’ for the Wrist
The link between obesity and high blood pressure is nothing new. Doctors established this connection as early as the 1940s [3]. Add to this increased blood lipids and a disturbed carbohydrate metabolism (also known as pre-diabetes) and you have what is known as metabolic syndrome. This is regarded as a decisive risk factor for arterial vascular disease. The metabolic syndrome is therefore one of the most common causes of high blood pressure today. For this reason, the usefulness of regular blood pressure measurements was proven early on [3]. The good thing is that nowadays this can be done at the doctors, but - thanks to smartwatches and the like – also conveniently at home.
Metabolic syndrome is a combination of risk factors such as abdominal fat, high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar and unfavourable blood lipid levels. Together they significantly increase the risk of cardiovascular disease and diabetes. The more of these factors are present, the higher the health risk. The syndrome can be prevented through a balanced diet, regular exercise, weight control and regular health checks.

HUAWEI WATCH D2
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring Precisely manage your health every moment
All-round Health Management
Light and Slim Design
Smart Living Experience Bluetooth calling, music playback and more
Medically Certified
Compatible with iOS and Android

Identifying the Possibility of High Blood Pressure -
24-Hour Blood Pressure Measurement with a Smartwatch
A single measurement is simply not enough to detect high blood pressure. As a rule, the 24-hour blood pressure measurement method, also known as Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring (ABPM), is used. This involves measuring blood pressure at regular intervals over a 24-hour period - even during sleep. This type of measurement represents the gold standard in the medical field [4].
Reminder: What is Blood Pressure?
In order for blood to flow effectively through the body and supply all organs and tissues adequately, the body needs the right blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force that the blood exerts on the walls of the arteries and veins as it flows through our body.
The new HUAWEI WATCH D2 is now the first smartwatch to enable ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. I recently tested the predecessor model – the HUAWEI WATCH D - on myself and on test subjects and was impressed by the gap that Huawei has closed in the wearables sector with this smartwatch. Ever since Riva-Rocci invented the easy-to-use cuff-based version of the mercury sphygmomanometer for the measurement of blood pressure, blood pressure has most commonly been measured using an integrated blood pressure cuff in the armband. This is an absolutely unique feature in the field of these smartwatches [4], and therefore Huawei is setting new standards with the automatic measurement function of blood pressure.
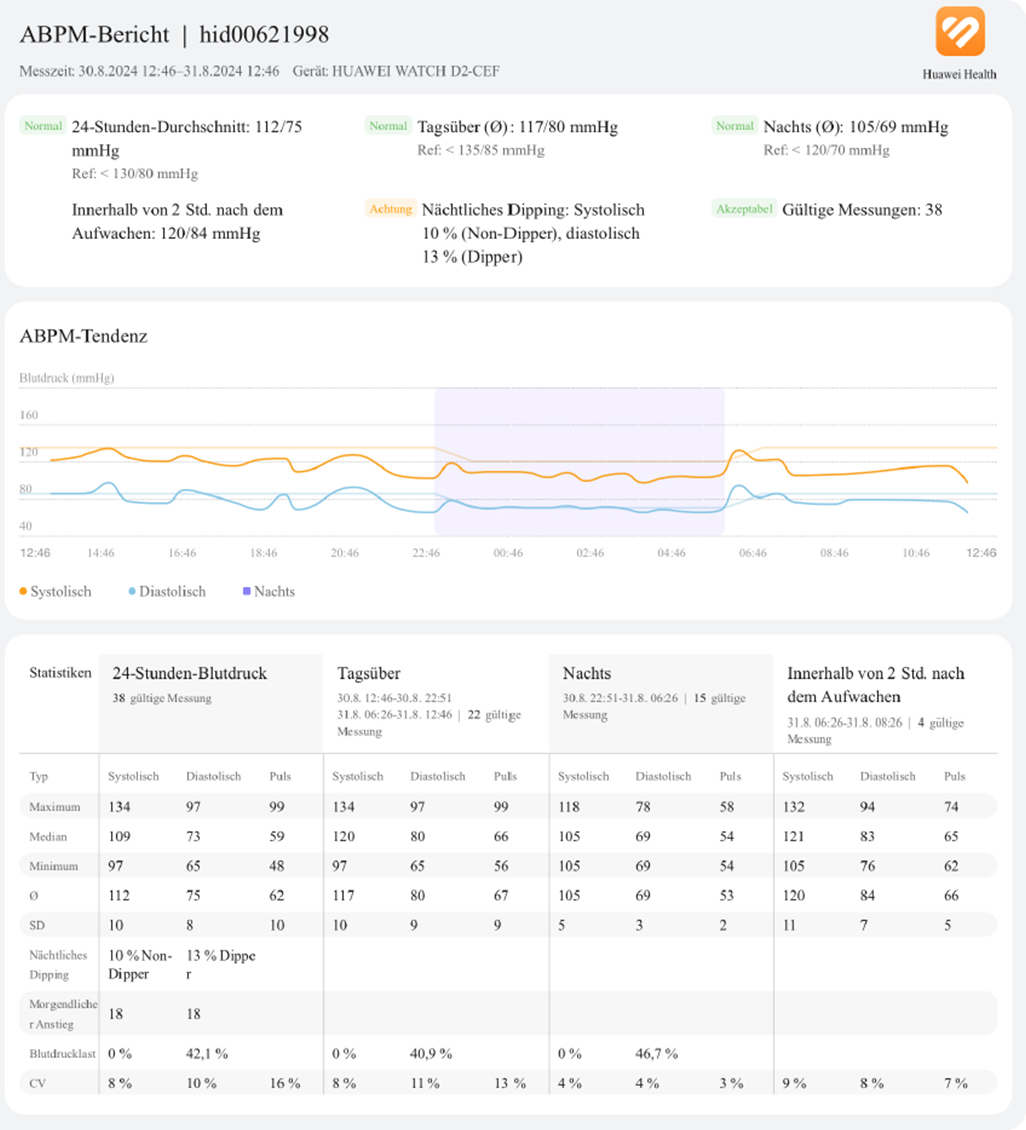
Blood Pressure Measurement Day and Night - The Practical Test
Let's get to the exciting questions: How does the HUAWEI WATCH D2's 24-hour blood pressure measurement (ABPM) work, and will it bother me? The result: I am very impressed! Whether during the day or at night, the HUAWEI WATCH D2 has integrated itself into my everyday life.
My Personal Plus Points:
+ Mini pump: This does its work absolutely silently. You can only hear the quiet inflow of air if you listen very carefully.
+ Comfort: The watch is comfortable to wear on the wrist and exerts little pressure.
+ Optics: I like the filigree case and the slim strap with the thin blood pressure cuff and the matt clasp straight away. This makes the first generation of the watch look a bit clunky, in comparison.
+ Function: The time window for the 24-hour measurement can be customised by the user and reminders for the regular measurement appear during the day, as a standardised sitting position must be adopted to ensure the measurement standards.
+ Correct measurement: The HUAWEI WATCH D2 also determines correct values at night depending on the sleeping position.
+ Restful sleep: In the morning, the watch shows me a complete log of blood pressure measurements made every 30 minutes. Impressive, because the pump didn't wake me up once during the night.
Good to know: Blood pressure – What is Normal and What is Elevated?
The Deutsche Hochdruckliga e.V. defines values for normal and high normal blood pressure, as well as high blood pressure. These values apply to a measurement taken in a sitting position and at rest after a few minutes of relaxation.
Optimal:
<120 mmHg (systolic) and <80 mmHg (diastolic)
Normal: 120-129 mmHg (systolic) and/or 80-84 mmHg (diastolic)
Elevated: 130-139 mmHg (systolic) and/or 85-89 mmHg (diastolic)
High blood pressure: From 140 mmHg (systolic) and/or from 90 mmHg (diastolic)

What to Do if You Have High Blood Pressure
As a doctor, it is clear to me that any form of high blood pressure should first be assessed by a medical professional. If regular measurements indicate high blood pressure, medication may not always be needed, but it is often necessary. The first and simple rule is: listen to your body and work on yourself.
However, an improvement in blood pressure values can also be achieved by adjusting your lifestyle. Important factors here are:
•Nutrition
o The ‘Mediterranean cuisine’ is a popular method of achieving a balanced diet as it emphasises vegetables, fruit and fish, as well as ‘good’ oils, like Omega 3.
o Olive oil, garlic, kale, horseradish, spinach, beetroot, apricots, rhubarb and nuts, as well as coconut milk and tomato paste, are considered natural blood pressure reducers.
o Your diet should be healthy and balanced, try to avoid food products high in fat and sugar.
o Reducing salt intake is widely known to help lower blood pressure. Natural, unprocessed foods are naturally low in salt (meat, eggs, milk, cereals, fruit, vegetables).
o ‘Ready-made products’ like bread, sausages and cheese, on the other hand, are high in salt and should therefore only be consumed in small quantities.
•Sport
o Regular exercise (>150 min/week) can help to lower blood pressure [5].
o Both endurance and weight training are beneficial towards healthy blood pressure values, as well as a combination of both.
•Weight reduction:
o If you are already overweight, a weight reduction of 10kg alone can reduce the systolic value by around 15mmHg and the diastolic value by 8-10mmHg.
Obesity is linked to high blood pressure and high blood pressure is linked to the likelihood of suffering a heart attack.
However, if you want to reduce your risk of a heart attack, you don't just have to reduce your weight but should specifically target your belly fat.
A prominent study from INTERHEART already established a link between waist circumference and the risk of heart attack in the early 2000s [6].
The following tips only represent a general wellbeing lifestyle recommendation. Please do not take them as medical advice.
Can the HUAWEI WATCH D2 help with weight loss?
The HUAWEI WATCH D2 has its own ‘Health Management’ section in the HUAWEI Health App. The app provides the user with information on calorie consumption (basal metabolic rate, sport, exercise) and also offers the option of documenting total calorie intake. It is also helpful to create a diet log. A separate watch face for calorie consumption reminds the user of their personal goals every time they look at the watch. The app also offers an interval fasting and weight optimization option, which can be very helpful.
My advice to my patients is that life should also be fun. You can eat ‘unhealthy’ food sometimes, but everything should be eaten in moderation. Don’t forget that regular exercise also helps prevent and treat high blood pressure.


For home use and outside of a doctor's office, there is no better 24-hour blood pressure monitoring device than the HAUWEI WATCH D2 in my opinion

What Else Can the HUAWEI WATCH D2 Do?
As you know from my blog about the HUAWEI WATCH 4 Pro Space Edition the Health Glance is now integrated. With ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) as the watch’s star feature, the HUAWEI WATCH
D2 is now a complete ‘health tool’ for me.
As a reminder, these 6 functions are already integrated in the watch:
● Heart rate
● SpO2
● Stress
● Skin Temperature
● Stiffness of the blood vessels
● Breathing test
As a passionate triathlete, I took the HUAWEI WATCH D2 with me for a regeneration running session after measuring my blood pressure over 24 hours. Here, too, the watch cuts a fine figure, delivers accurate values and is pleasantly light to wear.

As a reminder, there are two different types of high blood pressure:
• Primary hypertension, which usually occurs with increasing age without any recognisable cause (90% of cases).
• Secondary hypertension occurs due to other underlying diseases and is much rarer.
Conclusion: A Useful ‘Health Tool’ for the Wrist
The HUAWEI WATCH D2 is a great further development of the first generation with a unique feature: 24-hour blood pressure measurement, also commonly known as ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM).
This measurement can be shown for self-monitoring purposes but can also be used as a reference when consulting a doctor.
The HUAWEI WATCH D2 wears like a ‘normal’ smartwatch and offers all the functions that are currently required – but with even more. No other smartwatch on the market currently offers ambulatory blood pressure monitoring.
Medical disclaimer: The HUAWEI WATCH D2 and the ECG feature is intended to be used by people aged 18 years and over, but is not intended to replace any medical diagnosis or treatment. Data obtained during the use of this device and feature is for personal reference only. Before using the device, please carefully read the Quick Start Guide, Wearing Guide, and Instruction for Use.
Due to national restrictions on obtaining approval / registration as a medical device, the Huawei WATCH D2 will only be available in selected European markets, and the ECG feature only works on watches and smartphones purchased in countries where the service is available
- Supported smartphones: Mobile phones with Android 6.0 or compatibles, HarmonyOS 2.0 or compatibles, or iOS 12.0 or compatibles. The Huawei Health app version on your mobile phone must be 11.0 or compatibles. Please make sure that your wearable device and phone are running the latest versions before using ECG.
-Heart rate, SpO2, stress, arterial stiffness, the breathing test and skin temperature are not medical device features, monitoring data and results are for reference only and should not be used as a basis for medical diagnosis or treatment.
References:
- 1. Schienkiewitz et. al. (2022): Übergewicht und Adipositas bei Erwachsenen in Deutschland - Ergebnisse der Studie GEDA 2019/2020-EHIS
- 2. Köchli et. al. (2019): Obesity, High Blood Pressure, and Physical Activity Determine Vascular Phenotype in Young Children
- 3. LEVY et. al. (1946): Overweight; its prognostic significance in relation to hypertension and cardiovascular – renal diseases
- 4. Hermida et. al. (2015): Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring (ABPM) as the reference standard for diagnosis of hypertension and assessment of vascular risk in adults
- 5. Wang et. al. (2022): A novel blood pressure monitoring technique by smart HUAMWEI WATCH: A validation study according to the ANSI/AAMI/ISO 81060-2:2018 guidelines
- 6. Wilding et. al. (2006): Obesity and risk of myocardial infarction: the INTERHEART study
- 7. Schneider et. al. (2023): Exercise characteristics and blood pressure reduction after combined aerobic and resistance training: a systematic review with meta-analysis and meta-regression
Administrator
Copied


