Blood Pressure Monitors:
HUAWEI Smartwatch
vs. Cuff-based Monitors

Reading duration: Approximately 6 minutes

Serge Kownator, MD
Serge Kownator, MD is head of the cardiovascular centre "Coeur de Lorraine" in Thionville, France and a specialist in cardiology and vascular diseases. He is a member of the French Society of Cardiology and a former member of the Congress Programme Committee of the European Society of Cardiology. He made a significant contribution to the 2011 and 2017 ESC guidelines on peripheral arterial disease and regularly speaks at international congresses, some of which he chairs.
In this article
What is Blood Pressure?
Why should you Measure your Blood Pressure?
Challenges and Further Developments in Blood Pressure Measurement
Huawei's WATCH D: Proven Medical Technology on the Wrist
How do I Recognise High Blood Pressure and its Symptoms with the HUAWEI WATCH D?

HUAWEI WATCH D2
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring Precisely manage your health every moment
All-round Health Management
Light and Slim Design
Smart Living Experience Bluetooth calling, music playback and more
Medically Certified
Compatible with iOS and Android

What is Blood Pressure?
Pressure or blood pressure is defined as the pressure within the arteries. This pressure allows
the blood to flow to the various organs in the body. This pressure is expressed by two numbers:
•The upper number on the screen of the HUAWEI WATCH D2 represents the
systolic pressure, i.e. the
pressure exerted on the arterial walls during the blood ejection phase associated with the
contraction of the heart.
•The lower number indicates the diastolic pressure, i.e. the
residual pressure that prevails in the arteries during the
relaxation or filling phase of the heart.
The Dynamics of Blood Pressure
Normally, blood pressure is higher during the day according to the different phases of activity,
while it drops at night
during the resting phase. It can rise sharply with any kind of stress or heavy exertion. It can
fall in hot weather and
rise in cold weather.
High blood pressure is present if the blood pressure at rest exceeds 140/90 mmHg in a clinical
setting, or 135/85 mmHg when measuring yourself
Good to know - Blood Pressure Values
Normal blood pressure is typically around 120/80 mm Hg (millimeters of mercury). It is important to note that depending on the time of day, blood pressure can sometimes fluctuate, often rising several hours before a person wakes up, peaking at around midday, and dropping in the late afternoon and evening. This can be easily checked at home using the HUAWEI WATCH D or HUAWEI WATCH D2, for example.
Why should you Measure your Blood Pressure?
High blood pressure is the most common risk factor for cardiovascular
diseases, especially strokes. According to the WHO, in 2025, 1.5 billion people between the ages
of 30 and 79 will be
affected by high blood
pressure, resulting in significant public health costs. Only half of patients with high blood
pressure receive
treatment, and of these, only half are treated effectively. Many people do not even realise that
they have high blood
pressure. Regular measurement, especially in menopausal women, is crucial to recognising and
preventing high blood
pressure [1,2].
How do you Measure Blood Pressure?
Nowadays, blood pressure is mainly measured in doctors' clinics,
hospitals and other medical facilities using three methods: the
auscultatory method with a stethoscope and sphygmomanometer, the
oscillometric method with automatic devices, or regular home blood
pressure monitoring.
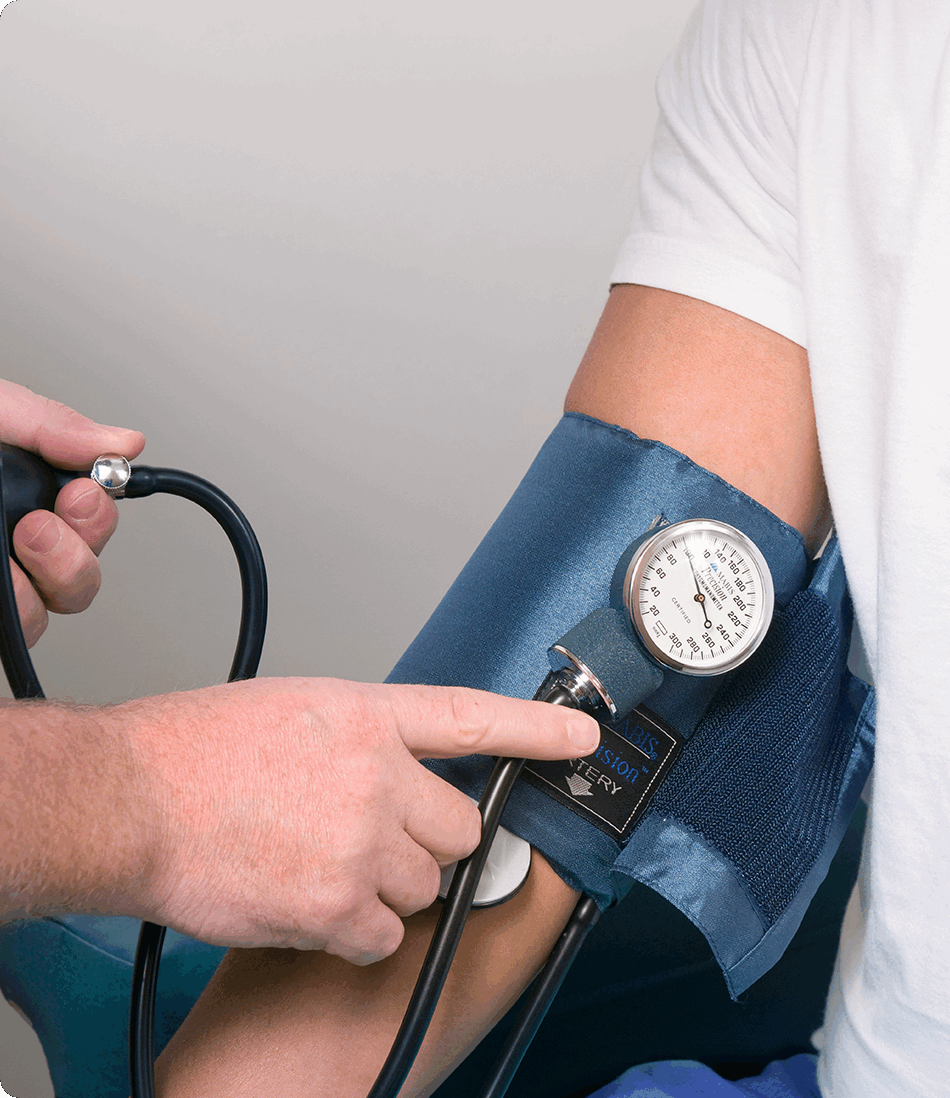
1. The auscultatory method is the main non-invasive reference method that
remains the method performed during a medical
consultation. It can be performed using a cuff connected to a sphygmomanometer. This method is
based on listening to the
arterial sounds with a stethoscope and has been used for over 100 years, in particular with the
Vaquez-Laubry
sphygmomanometer, which is named after its inventors (photos 1, 2).
2. Today, the use of an automatic electronic blood pressure monitor through the oscillometric
method is also commonly
used (photo 3).
Regardless of the method, the size of the cuff plays an important role in a meaningful
assessment.
3. In addition, regular and manual blood pressure monitoring
throughout the day is made possible HUAWEI WATCH D (photo 4), which
is of great benefit in special health situations
outside of a clinical setting.
4. With the introduction of the HUAWEI WATCH D2, users can now
benefit from enhanced monitoring capabilities, including the new ABPM feature,
which provides even more precise blood pressure tracking over a 24-hour period.

The evolution of blood pressure measurement from 1945 to the stylish
health device - the HUAWEI WATCH D2 in 2024.
Challenges and Further Developments in Blood Pressure Measurement
Blood pressure measurement data collected during a doctor's visit is the subject of much debate.
Doctor’s visits can inadvertently cause some patients stress, which may lead to blood pressure
values being different than from home, or another relaxed environment. Nowadays, measurement
methods outside of medical practices are increasingly recommended to support data collected by
health professionals in a clinical setting.
Recognising Symptoms of Hypertension Outside of the Clinical Practice - How Accurate are the
Measurements?
Blood pressure measurements outside the practice can either be self-measurements, which the
patient carries out
themselves according to a precisely defined protocol, or an automatic recording over 24 hours,
which is called
ambulatory blood pressure measurement (ABPM). The latter method can be used to recognise
particular forms of high blood
pressure, especially nocturnal high blood pressure.
Innovative technologies in blood pressure monitoring
In addition to traditional cuff-based blood pressure monitors, more and more so-called
"cuff-less" monitors (without a
cuff) are being developed, which are often integrated into networked objects and utilise
photoplethysmography (PPG)
technology. Here, the blood flow is recorded by measuring light changing and
absorption on the surface of the skin. The validation of this technology has not yet been
completed, and remains prone
to greater inaccuracies than other methods.

In case of hypertension, self-measurement allows an evaluation of the treatment efficiency. Beside the classical electronic device, the HUAWEI WATCH D appears as an easy and accurate device to assess the results of the treatment. With the introduction of the HUAWEI WATCH D2, users can now benefit from enhanced monitoring capabilities, including the new ABPM feature, which provides even more precise blood pressure tracking over a 24-hour period.
HUAWEI's WATCH D and D2: Proven Medical Technology on the Wrist

In addition to these wristband-less blood pressure measuring devices, the HUAWEI WATCH
D and HUAWEI WATCH D2 are particularly
noteworthy as it has an
inflatable pouch within the wristband. For the measurement, this pouch is inflated using a
mini-pump integrated into the
watch and an oscillometric method is applied. The observed
results of the blood pressure measurements are well validated, with deviations of ± 3 mmHg
compared to the reference measurements.
The measurement was taken within 30 seconds in a seated position, with the wrist at heart
level. The result of the
measurement is shown
immediately on the watch display and also transmitted to a smartphone if the Huawei Health
App is installed on it.
How do I Recognise High Blood Pressure and its Symptoms with a HUAWEI WATCH D and HUAWEI WATCH D2?

HUAWEI WATCH D2
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring Precisely manage your health every moment
All-round Health Management
Light and Slim Design
Smart Living Experience Bluetooth calling, music playback and more
Medically Certified
Compatible with iOS and Android

Measuring blood pressure with the HUAWEI WATCH D, as well as the
HUAWEI
WATCH D2, is easy to perform, and the results appear to be reliable. This makes it easy
to recognise high blood
pressure, monitor the effectiveness of treatment and take into account
fluctuations in blood pressure related to the environment, stress and general health.
Top results: The HUAWEI WATCH D enables simple and accurate
measurement of blood pressure values, with 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring
available on the HUAWEI WATCH D2.
The measurements obtained with the HUAWEI WATCH D were validated
in
several comparative studies using the standard method [3]. These studies showed absolutely
satisfactory correlations
without statistically significant
differences.
In conclusion and to summarise, high blood pressure, or hypertension, is a highly important risk
factor for cardiovascular disease. In most cases, it is not recognised. Although the diagnosis and
treatment are the responsibility of the doctor, people play an important role in the detection of
hypertension, as well as in the
effectiveness of treatment when it occurs. I would recommend using a HUAWEI WATCH D or HUAWEI WATCH
D2 as a method of self-measurement due to its ease of use and reliability. Compared to
conventional measuring devices, it is intuitive and easy to use.
In addition to blood pressure functions, the watch offers a whole range of health applications,
including ECG, heart rate, activity monitoring, and much more, which not only supports heart health
but also provides a well-rounded overview of one’s health situation on the wrist. The HUAWEI WATCH
D2 further enhances this with APBM and 24-hour continuous monitoring.
Medical Disclaimer:
HUAWEI WATCH D and HUAWEI WATCH D2 are
intended to be used by people aged 18 years and over, but is not intended to replace any medical
diagnosis or treatment. Data obtained during the use of this device and feature is for personal
reference only. Before using the device, please carefully read the Quick Start Guide and Wearing
Guide and Instructions for Use.
Due to national restrictions on obtaining approval / registration as a medical device, HUAWEI WATCH
D and HUAWEI WATCH D2 will only be available in selected European markets, and the ECG feature only
works on watches and smartphones purchased in countries where the service is available.
- Supported smartphones: Mobile phones with Android 6.0 or compatibles, HarmonyOS 2.0 or
compatibles, or iOS 12.0 or compatibles. The Huawei Health app version on your mobile phone must be
11.0 or compatibles. Please make sure that your wearable device and phone are running the latest
versions before using the device.
Heart rate, SpO2, stress and skin temperature are not medical device features, monitoring data and
results are for
reference only and should not be used as a basis for medical diagnosis or
treatment.
[References]
- 1. Mancia G, Kreutz R, Brunstrom M, Burnier M, Grassi G, Januszewicz A, et al. 2023 ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension: endorsed by the International Society of Hypertension (ISH) and the European Renal Association (ERA). J Hypertens 2023;41:1874-2071.
- 2. Kreutz R, Brunström M, Burnier M, Grassi G, Januszewicz A, Muiesan ML, Tsioufis K, de Pinho RM, Albini FL, Boivin JM, Doumas M, Nemcsik J, Rodilla E, Agabiti-Rosei E, Algharably EAE, Agnelli G, Benetos A, Hitij JB, Cífková R, Cornelissen V, Danser AHJ, Delles C, Huelgas RG, Járai Z, Palatini P, Pathak A, Persu A, Polonia J, Sarafidis P, Stergiou G, Thomopoulos C, Wanner C, Weber T, Williams B, Kjeldsen SE, Mancia G. 2024 European Society of Hypertension clinical practice guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur J Intern Med. 2024 Aug;126:1-15.
- 3. Zhang, Wei; Zhou, Yi-Ni; Zhou, Yi; Wang, Ji-Guang. Validation of the watch-type HUAWEI WATCH D oscillometric wrist blood pressure monitor in adult Chinese. Blood Pressure Monitoring, Volume 27, Number 5, 04 July 2022, pp. 353-356(4)
Administrator
Copy successful


