HUAWEI TruSportTM
Research System

current running
ability?
wearables to
determine the right
exercise intensity for
you?
appropriate training
time.
periodic training plan
that fits your current
ability and desired
goals.
running posture.
athletic ability assessment system.

your current
running ability?
The Running Ability Index calculates your highest levels of endurance and running technique and predicts how well you will perform in competitive running.
To implement, wear your HUAWEI wearable device with heart-rate monitoring and GPS turned on when out on a run. Your Running Ability Index is based on your detected pace, heart rate and other data, without the need to run at maximum intensity. Once your run is over, you can instantly view your index and discover your current running ability.

| Running Ability Level | Performance | Running Ability Index |
| Marathon World Record | 2:01:39 | 85.3 |
| 2.5-Hour Marathon | 2:30:00 | 69.2 |
| 3-Hour Marathon | 3:00:00 | 56.4 |
| 3.5-Hour Marathon | 3:30:00 | 46.7 |
| 4-Hour Marathon | 4:00:00 | 40.7 |
The Running Ability Index is designed to give users an indication of how well they will perform in running competitions of different distances. Based on the Running Ability Index, the runners' 5km, 10km, full marathon and half marathon running results can be predicted, which can help runners understand their level and better prepare for the race.


The heart rate zone for running training is usually measured by the heart rate reserve, which takes into account the resting heart rate and can better match individual training requirements. Heart rate reserve refers to the range of heart rate that can be reached during exercise, defined as the maximum heart rate reached during exercise minus your resting heart rate. Equation for calculating heart rate reserve interval: heart rate reserve percentage of the interval * heart rate reserve + resting heart rate.

Pace zone refers to the division of running pace into different intervals. These intervals can be used to measure training intensity and are used to guide running training for specific purposes. There is a corresponding relationship between the pace zone and the heart-rate zone. However, when the intensity requirements are switched during training, there is can be a differential between the actual exercise heart rate change and the pace. At this time, you can refer to the pace zone as the basis for training intensity.
The division of the pace zone is related to the Running Ability Index. The different value ranges of different runners in the same pace zone roughly reflects their differing levels. During a runner's training period, both the running performance and the Running Ability Index will change. At this time, you can also re-calculate and set the pace zone based on this new data.


appropriate training time
exercise, training pressure and post-workout recovery, and provides a reference for daily running training. For advanced runners and elite runners, a long-term system training process is provided.
The physical fitness/fatigue index and the current training performance evaluation data updates over time, helping you train at a reasonable pace, step by step, and scientifically improves your performance.


Training Stress

Recovery time refers to the time required to fully recover from fatigue caused by training stress. The degree of recovery reflects the degree of physical recovery after a single training session. High-stress training stimulation requires a longer recovery time. The length of recovery time is calculated based on any remaining recovery time prior to an exercise plus the level of training stress caused by the latest workout.


Recovery heart rate refers to the difference between the heart rate at different time periods and the peak heart rate during exercise. The speed of heart rate recovery after exercise can be used to measure a runner's ability to adapt to the training load. The faster a runner's heartbeat recovers after exercise, the higher the aerobic capacity. Huawei wearable devices automatically calculate and record the recovery heart rate 1 to 2 minutes after the end of the activity, and evaluate aerobic capacity and physical recovery capacity.

Maximum oxygen uptake (VO2 Max) refers to the amount of oxygen used by the body per unit of weight per unit of time during maximum load exercise. The maximum oxygen uptake is an important indicator of aerobic exercise capacity. Generally speaking, the higher the maximum oxygen uptake, the higher the efficiency of providing energy during exercise and the better the exercise performance. Traditional measurement methods require subjects to reach a state of exercise exhaustion. With the help of Huawei wearable devices, however, the maximum oxygen uptake can be accurately estimated based on PPG sensors and data. Maximum oxygen uptake is an important reference for endurance exercise evaluation, but is not the only indicator of performance. Development of overall physical fitness, mastery of technique, and scientific and systematic training are all key to improving performance.


Performance
Estimate
| Explanation and Suggestions | |
| exellent | After the targeted training phase, the exercise performance is adjusted to the best state through training reduction, and it is an ideal time to participate in the competition or test. |
| good | The body recovers from the fatigue of training for good exercise performance. |
| normal | In lightweight periodic training, the corresponding training can be easily completed in this range. |
| poor | The body has built up a certain amount of fatigue, and can feel the effects of training pressure. Reduction or rest is usually recommended; however, as periodical training, it is sometimes necessary to purposely increase the training load for a period of time, and adjust the training to this state, so that the training index can increase significantly after the reduction period. |
| very poor | Training is beyond the body's tolerance, and rest is recommended. |



A well-designed training plan should see a gradual increase in training load, in order to most effectively improve athletic ability. If the training load increases suddenly, the body needs more time to adapt, thus undermining the effectiveness of the training. The increase in the training load will also increase chance of injury. But a training load that does not increase will make the body's ability improvement become insignificant after the body adapts.
For example with marathon training, the total training plan is divided into a base period, an improvement period, a consolidation period, and a weight reduction period. Workouts for each stage are formulated to achieve specific training objectives.
| Period | Training Purpose | Main Course Schedule | ||
| Initial | Training adaptation, basic endurance | Easy running, aerobic running, middle distance jogging, etc. | ||
| Upgrade | Improve the VO2 Max level and aerobic endurance |
High-intensity interval, aerobic running, long-distance jogging, etc. | ||
| Consolidation | Improves lactate tolerance and long-distance aerobic endurance |
Rhythm running, cruising interval running, long distance jogging, etc. | ||
| Reduction | Pace adaptation and adjustment of pre-match state |
Marathon pace running, easy running, etc. |



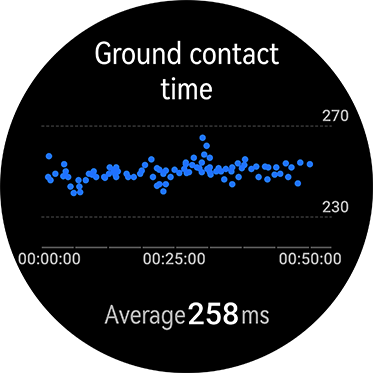
One step time (1/step frequency) = hang time + ground contact time
When running, forward movement is only achieved when the feet are off the ground, therefore the longer your shoes are in contact with the ground, the poorer the running efficiency.
In order to improve your running efficiency, therefore, decreasing ground contact time is key. Comparing your ground contact time before and after a period of training is vital for charting training efficacy.

Vertical oscillation refers to the height of the vertical movement of the body's center of gravity during exercise. Generally speaking, the larger the oscillation, the more energy wasted. When skipping rope, for example, no matter how high the jump, no forward motion is achieved, increasing the burden on the muscles. Therefore, the higher the oscillation, the worse the efficiency and the greater the impact force on the foot, bring ing a greater risk of injury.
However, if vertical oscillation is too low, it can cause a decrease in flight time, reducing the size of the stride and the decreasing speed. Therefore, maintaining a low vertical oscillation while also maintaining large strides is the goal of elite runners. When two runners are running at the same pace, the runner with a lower vertical oscilation enjoys higher efficiency, lower muscle output, and less risk of fatigue and/or injury.
Some runners will notice a decrease in the vertical oscillation due to the weakness of their legs after fatigue, so this type of runner should add strength training to their regimen.
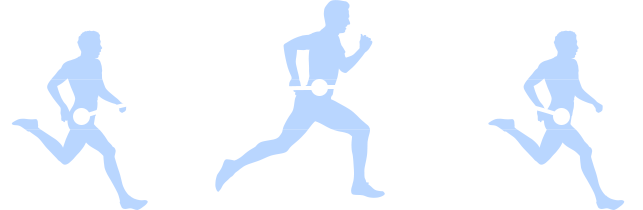


Desirable swing angles:
• Greater than 70 degrees when jogging
• Between 90 and 110 degrees at medium speed
• Greater than 110 degrees at high speed
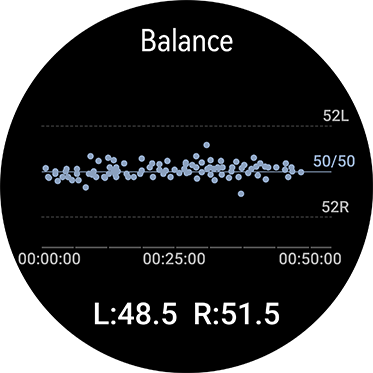
•> L51.5
- The left foot touches the ground for a long time
•L50.6-L51.5
- Touch time for the left foot is slightly longer
•L50.5-R50.5
- Left and right ground contact time balance
•R50.6-R51.5
- The touch time for the right foot is slightly longer
•> R51.5
- The right foot touches the ground for a long time